Xu Feng offer rapid tooling service, when you are looking for a supplier to meet following requirements, you can consider our quick turn tooling solution.
► Moderate production volumes: rapid tooling is well-suited for producing moderate quantities of parts, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands. It strickes a balance between cost-effectivness and speed for such production volumes.
► Similar part structures: if parts have similar structures or share common design elements, rapid tooling can be more efficient as it levarages optimized design and fabrication processes.
► Portotyping and Iterative design: In the early stage of product development, when prototypes or iterative design changes are frequent, rapid tooling allows for quicker adjustments and modifications to the tooling and parts.
► Martket testing and product launch: for maket testing or lauching a new product where getting to market quickly is crucial, rapid tooling provides a fast route to producing the intial batches of parts.
► Dynamic production requirements: in situations where demand is subject to change, and production needs to adapt quickly to fluctuations, rapid tooling allows for a more agile response to shifting requirements.
► Cost sensitivity for moderate quantities: when cost considerations are important, and the production quatity falls within the moderate range, rapid tooling can offer a more economical soution compared to traditional tooling methods.
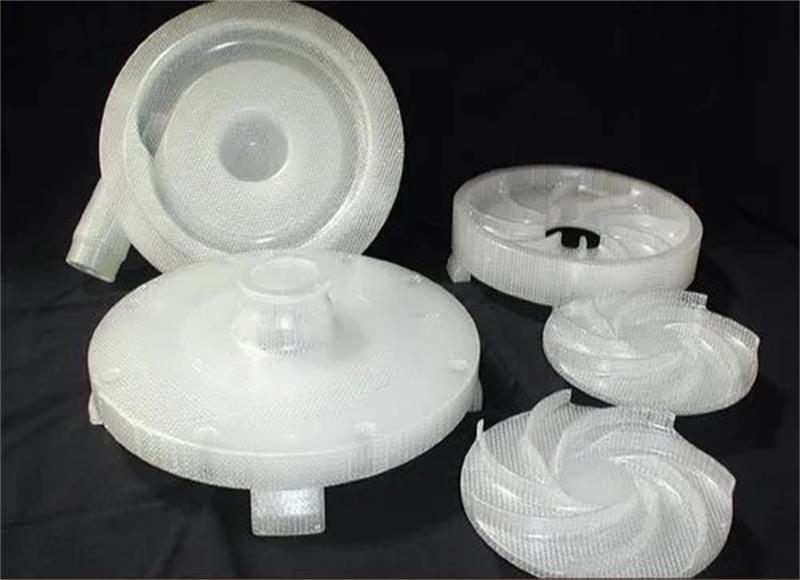
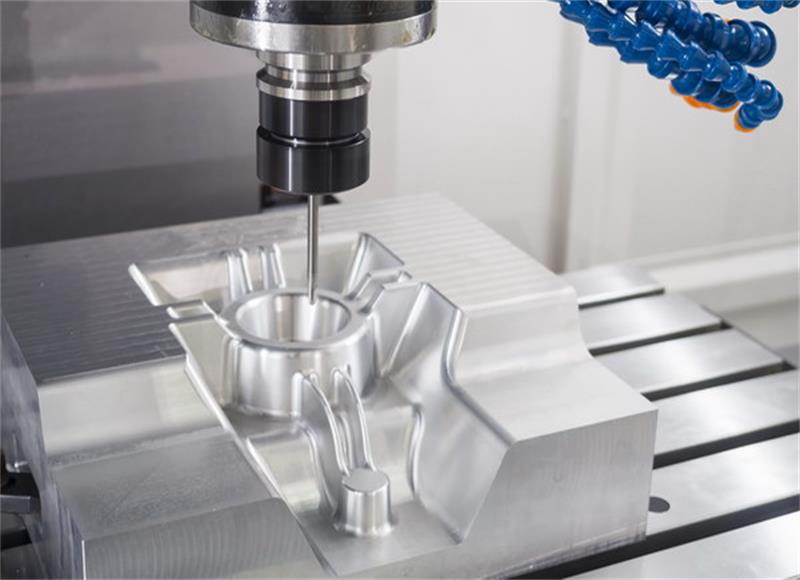
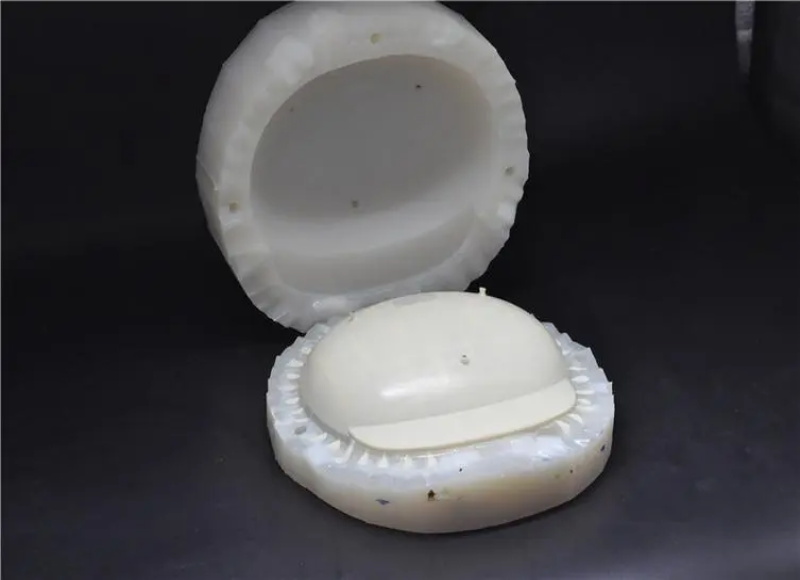



Rapid tooling refers to the process of quickly manufacturing tooling, such as molds or dies, to produce prototypes parts or low to moderate production volumes. The primary goal of rapid tooling is to reduce the time and cost associated with traditional tooling methods, allowing for faster iteration in product development or quicker respondse to market demands.
Product Development: Rapid tooling is integral in the early stages of product development, allowing designers and engineers to quickly test and refine designs.
Bridge to Production: It serves as a bridge between prototyping and full-scale production, enabling the production of limited quantities of parts without the need for expensive, high-volume tooling.
At Xu Feng, we can provide the rapid tooling include
Aluminum is chosen for its excellent machinablility, relatively low cost and good thermal conductivity, these properties make it well suited for rapid mold. It strikes a balance between speed, cost-effectiveness and durability, making it a valuable tool in prototyping and low-volume production.
| Recommend material for aluminum mold 7075 Aluminum: the best material for aluminum mold, it has high strength and hardness, make it suitable for high-stress applications, such as injection molds for moderate volume production. 6061 Aluminum: Often used for molds where moderate strenth and good corrosion resistance are required, it's suitable for low to moderate production volumes. 2024 Aluminum: Suitable for molds where high strength is a primary consideration. |
Soft mold typically refers to a mold made from materials that are more flexible or less rigid than traditional steel. Soft mold is used for prototyping or small productin runs. Production runs using soft mold typically produce about hundreds pieces of parts.
| Recommend material for soft mold Silicone Rubber: Silicone is a common material for soft molds due to its flexibility, high tear strength, and ability to capture intricate details. Polyurethane (PU): Polyurethane materials can be used to create soft molds, offering flexibility and ease of handling. Latex: Latex is another flexible material used for making molds, particularly in applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial. |
Rapid prototyping with 3D print enable you to print prototypes within a day and carry out multiple iterations of design, size, shape, or assembly based on results of real-life testing and analysis, helping you to bring better products to market faster.
| Recommend material for 3D print Nylon: Used for casings, housings, consumer sports equipment, intricate prototype plastic parts, and prototypes with specific shapes, assemblies, or functionalities. Photosensitive Resin: Applied in the fields of household appliances, rapid manufacturing, prototype modeling, electronic products, educational research, architectural models, art models, and automotive manufacturing. Wax (Red Wax): Widely employed in the creation of figurines, animations, exquisite artworks, and jewelry exhibits. |
Speed and Time Savings:
Rapid Tooling allows for quick turnaround times, it will shorten from months or weeks than Conventional Harden Tooling, enabling faster product development and time-to-market.
Cost Efficiency:
Rapid tooling techniques often involve less material waste, and the overall cost is generally lower compared to traditional methods, especially for low to medium production volumes.
Flexibility and Iteration:
Rapid tooling provides the flexibility to make design changes easily. This is particularly valuable during the prototyping phase when design iterations may be frequent.
Risk Mitigation:
Rapid tooling allows for the creation of prototypes and small production runs before committing to full-scale tooling. This helps identify and address any issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of costly errors in mass production.
Tooling Life:
Rapid tooling materials may not be as durable as those used in traditional tooling, leading to a limited tool life.
Tolerance and Precision:
Achieving tight tolerances can be challenging in rapid tooling parts.
The precision of the final parts may be lower compared to parts produced using traditional tooling methods.
Volume Limitations:
Rapid tooling is generally more suitable for low to medium production volumes.
High-volume production may be more cost-effective with traditional tooling methods.
It's important to note that the choice between rapid tooling and traditional tooling depends on factors such as project requirements, production volumes, and budget constraints.